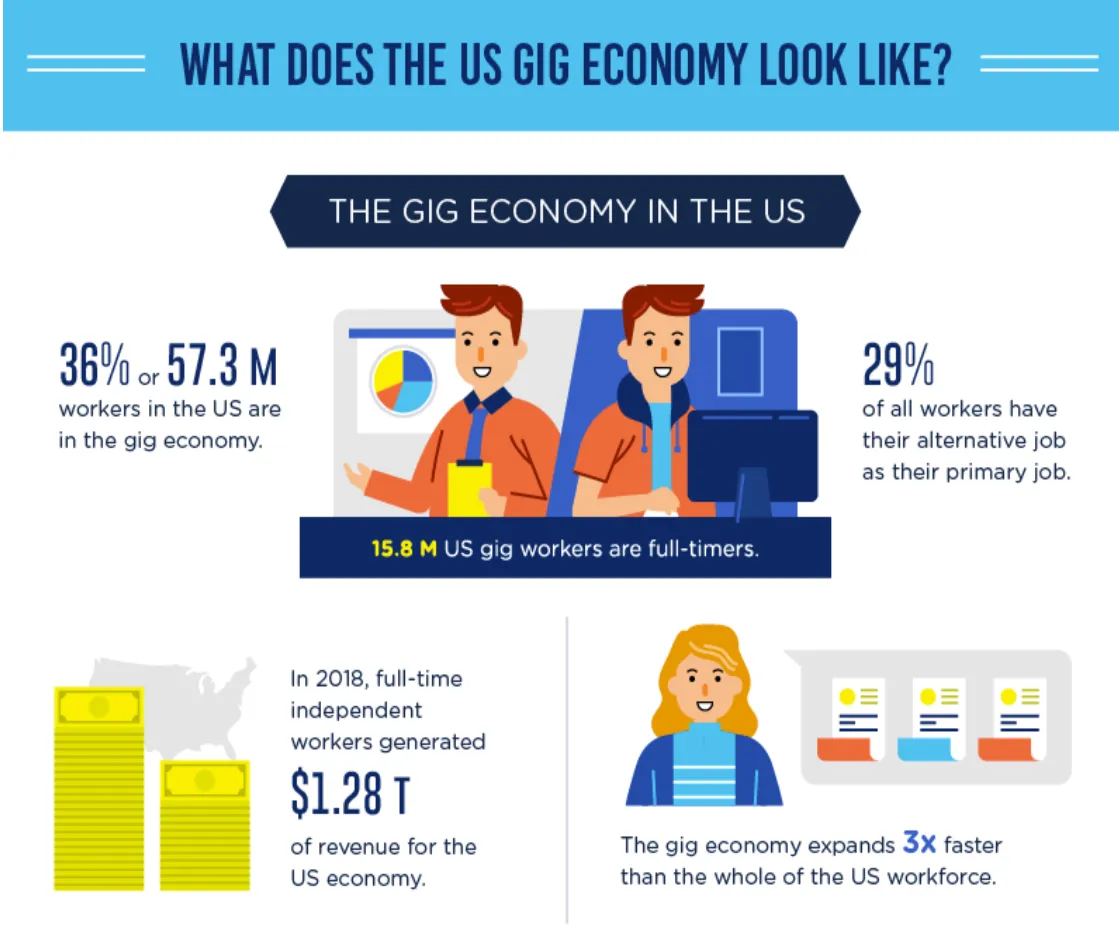
The gig economy in the United States is a dynamic and rapidly evolving sector characterized by the proliferation of short-term, freelance, and on-demand work opportunities. Here’s a snapshot of what the US gig economy looks like:
1. Diverse Work Opportunities: The gig economy encompasses a wide range of job categories and industries, including ride-sharing, food delivery, freelance writing, graphic design, web development, personal shopping, and more. Workers in the gig economy can find opportunities across various sectors.
2. Flexible Work Arrangements: Gig workers enjoy a high degree of flexibility in terms of when and where they work. They can often set their own schedules, allowing them to balance work with personal commitments.
3. Technology-Driven Platforms: Technology platforms and mobile apps play a central role in connecting gig workers with customers or clients. Companies like Odds, Uber, Lyft, DoorDash, Upwork, and Fiverr provide the infrastructure for gig work.
4. Independent Contractors: Many gig workers are classified as independent contractors, which means they are responsible for their own taxes, benefits, and insurance. This arrangement provides autonomy but also requires workers to manage their financial affairs independently.
5. Part-Time and Side Hustles: The gig economy is not limited to full-time work. Many participants engage in gig work as a part-time or side gig to supplement their income from traditional jobs.
6. Diverse Workforce: Gig workers come from a variety of backgrounds and demographics. They include college students, retirees, stay-at-home parents, freelancers, and individuals seeking to diversify their income sources.
7. Earnings Variation: Earnings in the gig economy can vary widely based on factors like location, demand for services, and the level of effort put in by the worker. Some gig workers earn a substantial income, while others use it as a supplementary source of income.
8. Emerging Gig Benefits: While gig work lacks many traditional employment benefits like health insurance and retirement plans, some companies are exploring new ways to provide gig workers with access to benefits such as insurance, retirement savings plans, and discounts on goods and services.
9. Global Gig Economy: The gig economy is not confined to the United States; it’s a global phenomenon. Many of the platforms that facilitate gig work operate internationally, enabling workers to take on tasks or jobs from anywhere in the world.
10. Economic Impact: The gig economy contributes to the overall economy by providing opportunities for income generation and consumer convenience. It also allows businesses to scale more efficiently and adapt to changing demands.
In summary, the US gig economy is a multifaceted and growing sector that offers diverse work opportunities and flexibility for participants. While it has its challenges and controversies, it continues to be a significant part of the labor market and reflects the changing nature of work in the 21st century.